基本原理
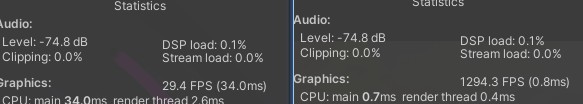
ComputeShader是专门用于大量并行计算的技术,在图形渲染中经常需要用到,其主要原理是通过多线程将大量并行计算从CPU转移到GPU中,既能加速计算也能节约GPU资源,在屏幕后处理中的自动曝光效果就用到了该技术来快速计算每帧的屏幕平均亮度
其线程结构如下图:
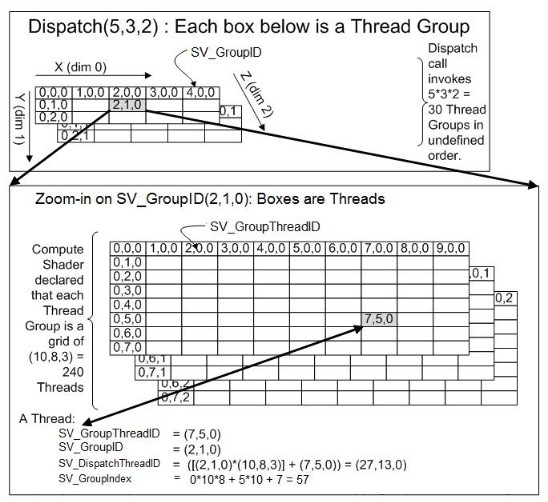
其中Compute.Dispath的三个参数分别为线程组的x,y,z, (5,3,2)表示一共有5*3*2个线程组,而每个线程组的大小由numthreads的x,y,z决定,其最大数量为1024(SM5.0).也就是说最多有1024个线程进行并行计算
其中调用ComputeShader的主函数时有四个重要参数
SV_GroupThreadID :是指该线程在该线程组的三维坐标,如图中在(7,5,0)的线程的SV_GroupThreadID就是(7,5,0)
SV_GroupIndex :是指该线程在该线程组的索引位置,如图中在(7,5,0)的线程的索引坐标就是 0*10(numthreads.x) *8(numthreads.x) + 5*10 + 7 = 57
SV_GroupID:是指该线程所在线程组的位置,如图中的线程组的SV_GroupID都是(2,1,0)
SV_DispatchThreadID: 就是指,该线程在所有组包含的线程中的位置,在图中在(7,5,0)的线程,GroupID是(2,1,0),先乘以numthreads.xyz即(10,8,3)然后加上 (7,5,0)得到(27,13,0)
应用实例
了解上述的基本原理后,需要在实际例子中应用,以下以自动曝光中的应用进行说明
C#部分(本案例中是在CommandBuffer执行的)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| //需要实例化ComputeShader
histogramCS = AssetDatabase.LoadAssetAtPath<ComputeShader>("Assets/Script/MyPostEffect/MyHistogram.compute");
//通过ComputeShader指定需要运行的Kernel
histogramKernel = histogramCS.FindKernel("CSHistogramMain");
//申明存储空间
ComputeBuffer histogramBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(k_Bins, sizeof(uint));
//将存储空间赋值给ComputeShader
cb.SetComputeBufferParam(histogramCS, histogramClearKernel, "_HistogramBuffer", histogramBuffer);
//其他输入参数的赋值
cb.SetComputeTextureParam(histogramCS, histogramKernel, "_Source", rtID);
cb.SetComputeVectorParam(histogramCS, "_ScaleOffsetRes", scaleOffsetRes);
cb.SetComputeFloatParam(histogramCS, "_DownSample", AEDownSample * 1.0f);
...
//触发ComputeShader,如果不进行降采样即AEDownSample = 1,需要处理1920 * 1080 份数据,一个线程组大小为16 * 16,因此一共120 * 68组线程组
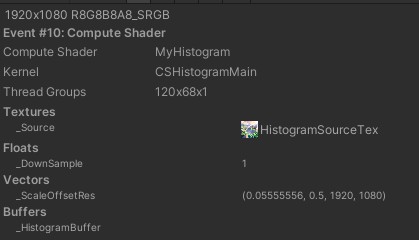
cb.DispatchCompute(histogramCS, histogramKernel, Mathf.CeilToInt(width / AEDownSample /16 ), Mathf.CeilToInt(height / AEDownSample / 16 ) , 0);
//可以从histogramBuffer中读取到ComputeShader的处理结果
int[] binData = new int[128];
histogramBuffer.GetData(binData);
|
ComputeShader部分
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| #pragma kernel CSHistogramMain
#include "Assets/PostEffect/Shaders/StdLib.hlsl"
#include "Assets/PostEffect/Shaders/Colors.hlsl"
#include "MyHistogram.hlsl"
#define SIZEX 16
#define SIZEY 16
#define GROUPSIZE SIZEX*SIZEY
//定义各种输入参数
RWStructuredBuffer<uint> _HistogramBuffer;
Texture2D<float4> _Source;
SamplerState sampler_LinearClamp;
float4 _ScaleOffsetRes;
float _DownSample;
//组间共享数组
groupshared uint gs_histogram[HISTOGRAM_BINS];
//定义numthreads大小
[numthreads(SIZEX, SIZEY, 1)]
void CSHistogramMain(uint2 dispatchThreadId : SV_DispatchThreadID, uint2 groupThreadId : SV_GroupThreadID, uint gidx : SV_GroupIndex)
{
//根据线程租中的索引坐标判断是否清空组间共享数组
if (gidx < HISTOGRAM_BINS)
{
gs_histogram[gidx] = 0u;
}
float2 ipos = float2(dispatchThreadId) *_DownSample;
//因为需要确保组件共享数组的数据情况,在统计前要同步所有线程
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();
if (ipos.x < _ScaleOffsetRes.z && ipos.y < _ScaleOffsetRes.w)
{
uint weight = 1u;
float2 sspos = ipos / _ScaleOffsetRes.zw;
float3 color = _Source.SampleLevel(sampler_LinearClamp, sspos, 0.0).xyz; // Bilinear downsample 2x
float luminance = Luminance(color);
float logLuminance = GetHistogramBinFromLuminance(luminance, _ScaleOffsetRes.xy);
uint idx = (uint)(logLuminance * (HISTOGRAM_BINS - 1u));
//将权重数据存入共享数组
InterlockedAdd(gs_histogram[idx], weight);
}
//要确保所有数据处理完毕,进行所有线程同步
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();
if (gidx < HISTOGRAM_BINS)
{
//将共享数组的数据统计到最终结果中
InterlockedAdd(_HistogramBuffer[gidx], gs_histogram[gidx]);
}
}
|
在FrameDebug中可以看到线程组的数量符合预期
应用效果
可以看到,在自动曝光中使用ComputeBuffer进行并行计算相较于直接通过在CPU端逐像素GetPixel来统计平均亮度,在运算效率上有显著提升